UN population report: Key takeaways for India and the world
Ancient and Medieval History
Art and Culture
Modern History
Post Independence History
World History
Indian Society
Physical Geography
Indian Geography
World Geography
Indian Polity
Governance
Social Justice
International Relations
Economics and Economic Development
Science and Technology
Environment and Biodiversity
Disaster Management
Internal Security
Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
Ethics Case Studies
Essay
Government Scheme
Daily Updates
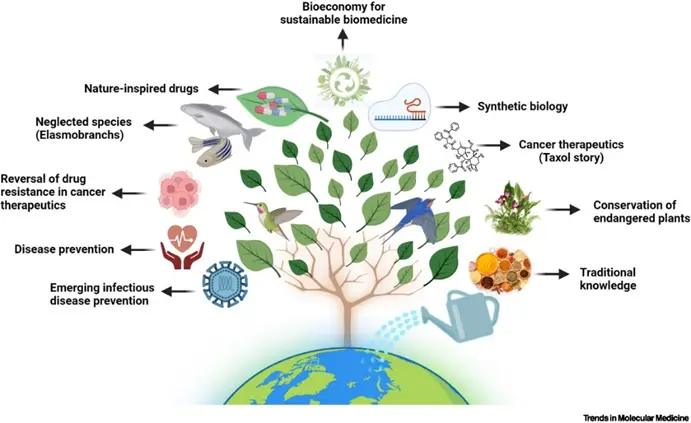
How biodiversity loss jeopardises human health

2023-04-10
10:12 am
487 Views
Biodiversity, encompassing animals, plants, and fungi, possesses a valuable reservoir of chemicals with potential applications in treating a range of diseases.
However, the decline of biodiversity is leading to species extinction, and with it, the loss of opportunities for medical breakthroughs.
Case Study - Poison Dart Frogs

- The vibrant colors of poison dart frogs, such as bright reds, yellows, and blues, serve as a clear warning to predators that the amphibians are toxic and consumption could result in convulsions, muscle contractions, and even death.
- The same toxic chemicals found on the frogs' skin have the potential to unlock new treatments for infections that have become resistant to currently available antibiotics.
- The poison dart frogs contain crucial medicinal compounds that serve as effective anaesthetics and antibiotics.
- Additionally, many other potentially beneficial chemicals found on the frogs have yet to be discovered or utilized commercially.
Importance of Biodiversity for much needed medicine
- Plants, animals, fungi and bacteria provide a range of chemicals that have the potential to treat various diseases, including malaria and cancer.
- Biodiversity supports the natural processes that are necessary for human survival.
- Natural compounds found on various species including frogs and plants form the basis for many important medicines.
- Examples include paclitaxel, derived from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, and ziconotide, sourced from cone snails, both used to treat cancer and severe pain respectively.
- The UN’s Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) states that approximately 70% of cancer drugs are derived from nature.
- However, biodiversity is rapidly declining, reducing the potential for new medicines.
- Climate change and chytrid fungus have resulted in significant declines in frog populations, leading to the extinction of numerous species.
- The chytrid fungus causes a disease that has wiped out up to 90 species of amphibians.
- Despite the possibility of not requiring such a vast array of frog species, the potential for new medicinal discoveries from the remaining biodiversity remains valuable.
Importance of Biodiversity in Drug Discovery in the Future
- There is much to be investigated in drug discovery, especially in the largely undiscovered ocean.
- Chemicals produced by sponges are being studied for treating cancers.
- Biodiversity is more than just individual species; it’s also about the interactions between them.
- William Gerwick from the University of California San Diego is investigating the symbiotic relationship between the weaver shrimp and cyanobacteria to find molecules that could be used to treat pancreatic cancer in humans.
- Losing biodiversity means losing access to unknown molecules that could save lives from infectious diseases and cancer.
Threats to Biodiversity and Extinction Rates
- The 2019 report by IPBES estimates that approximately 1 million animal and plant species are at risk of extinction due to human activities.
- Although the exact number varies according to different sources, experts agree that species are disappearing at a rate of 1,000 to 10,000 times faster than normal extinction rates.
- Overharvesting and land conversion are currently the biggest threats to biodiversity, including land clearance for food, livestock grazing, and ocean clearance.
- Since 1990, almost 420 million hectares of forest have been lost, equivalent to the size of the European Union, which has been converted into farmland or cleared for other uses.
- Fish stocks are also declining, with around one-third of global stocks estimated to be overfished in 2017.
- Human-driven climate change is another significant factor affecting biodiversity. Increasing levels of carbon dioxide are causing ocean acidification, leading to coral bleaching and the destruction of habitats.
- Rising temperatures and unsustainable harvesting practices are also pushing plant species to the brink of extinction.
Impact of Biodiversity Loss on Human Health
- Reduction in the number of species can lead to the loss of valuable medicinal resources.
- Extinction of a species may result in the permanent loss of valuable genetic information.
- The decline of biodiversity can have negative impacts on human nutrition and food security.
- Biodiversity loss is impacting how communities access traditional medicine.
- Approximately 4 billion people still rely primarily on natural remedies to heal themselves.
- When plants used in traditional medicine become difficult to access, it puts the health of these communities at risk.
- Around 40% of the world’s plant species are threatened with extinction, including 723 species used medicinally.
- The Pacific yew tree, which is the source of the chemotherapy drug paclitaxel, is now classified as near threatened under the IUCN Red List.
- Biodiversity loss doesn't just affect drug discovery but also has implications for human health globally.
Planetary health equals human health
- Humans depend on the natural world to maintain their health and wellbeing, including for drug discovery, air purification, clean water, and food production.
- Efforts are underway to protect biodiversity and prevent further loss, such as the agreement by 188 governments to protect 30 percent of the planet by 2030.
- However, it remains uncertain whether these measures will be sufficient and implemented quickly enough.
- Human health and planetary health are interconnected and interdependent.















Comments
Login To Comment
Recent Comments